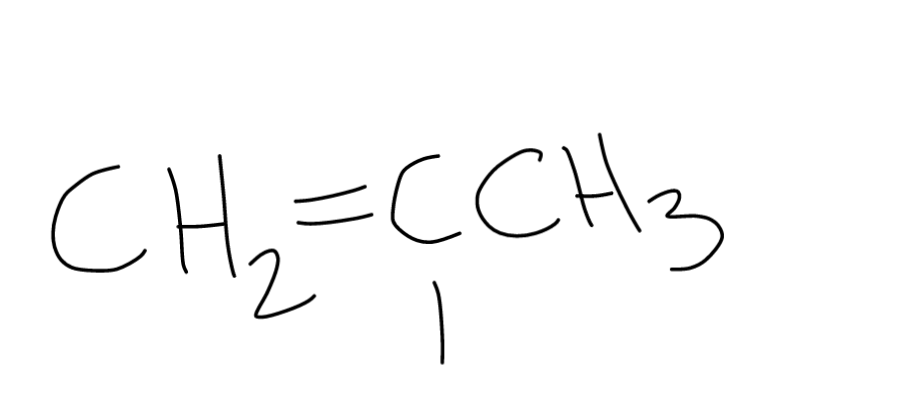Ch2 ch is called vinyl group so when a halogen atom is attached to this group it will be known as vinyl halide and when a halogen atom is attached to benzene ring it is known as aryl halide.
Difference between vinyl and aryl halides.
Summary alkyl halide vs aryl halide.
For this reason alkenyl halides with the formula rch chx are sometimes called vinyl halides.
The most important members are the aryl chlorides but the class of.
The main difference between alkyl and aryl is that alkyl group has no aromatic ring whereas aryl group has an aromatic ring.
In high dielectric ionizing solvents such as water dimethyl sulfoxide acetonitrile s n 1 and e1 products may be observed.
Allyl groups have three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms whereas v inyl groups have two carbon atoms and three hydrogen atoms.
Aryl halides are relatively unreactive toward nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Keeping eye on the structural difference of these functional groups we can easily differentiate it between them as allyl group holds three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms on the other hand vinyl group has two carbon atoms and three hydrogen atoms.
The r group in the structure can be any group with any number of atoms with any type of bonding pattern.
Rapid s n 2 substitution for 1º and 2º halides.
This lack of reactivity is due to several factors.
This conversation is already closed by expert was this answer helpful.
R in this case is any other group of atoms.
Formally this is ethylene h 2c ch 2 with one of the hydrogens substituted by a heteroatom.
For 3º halides a very slow s n 2 substitution or if the nucleophile is moderately basic e2 elimination.
What is the difference between alkyl and aryl.
What is aryl definition aryl group aryl halides 3.
The term vinyl is often used to describe any alkenyl group.
Steric hindrance caused by the benzene ring of the aryl halide prevents s n 2 reactions.
Alkyl halides and aryl halides are organic halides.
What is alkyl definition alkyl group alkyl halides 2.
An aryl halide has general formula c6h 5x in which an halide group x has substituted the aryl ring.
Vinyl chloride h 2c ch cl is an example.
Rapid s n 2 substitution for 1º halides note there are no β.
The simplest examples of an aryl halides are bromobenzene or chlorobenzene c6h 5x.
In organic chemistry a vinyl halide is a compound with the formula ch 2 chx x halide.
The key difference between alkyl and aryl halide is that the halogen atom in alkyl halides is attached to a sp 3 hybridized carbon atom whereas in aryl halides it is attached to a sp 2 hybridized carbon atom.
Likewise phenyl cations are unstable thus making s n 1 reactions impossible.